Understanding COPD: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a serious lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding COPD, its causes, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for both patients and their loved ones. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of COPD and explore ways to effectively manage this chronic condition.
What is COPD?
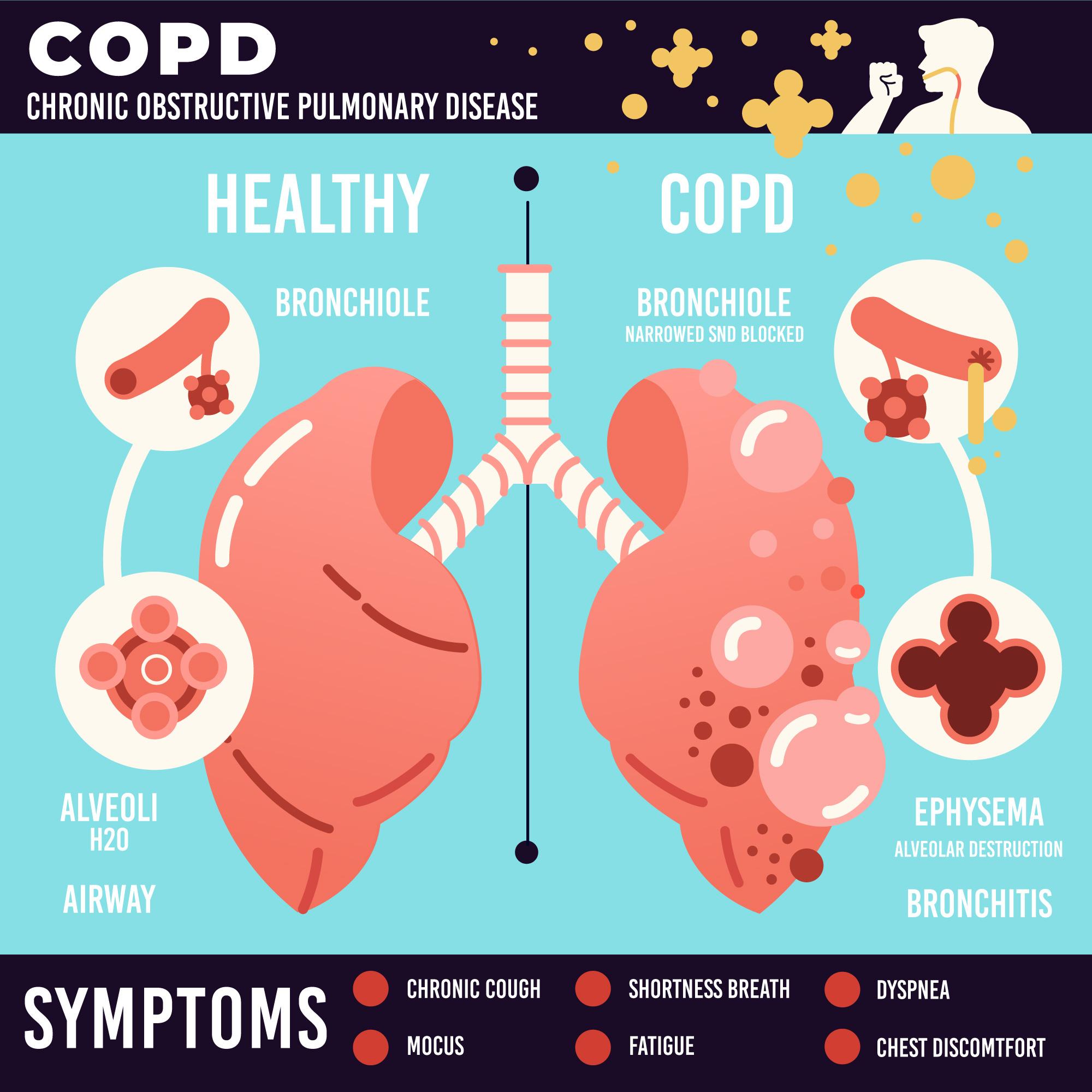
COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by obstructed airflow, making it difficult to breathe. The two main conditions that contribute to COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis involves long-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes, while emphysema damages the air sacs in the lungs, reducing their elasticity.
Causes of COPD
The primary cause of COPD is cigarette smoking. However, long-term exposure to other lung irritants such as air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust can also contribute to the development of COPD. In some cases, genetic factors may predispose individuals to the disease.
Symptoms of COPD
The symptoms of COPD often develop slowly over time and may worsen as the condition progresses. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Fatigue
- Bluish tint to the lips or fingernail beds (in severe cases)
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing COPD effectively. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, and imaging studies such as chest X-rays or CT scans.
Treatment for COPD aims to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. This may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking, avoiding lung irritants, and maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine.
- Medications: Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen therapy may be necessary for patients with severe COPD to improve oxygen levels in the blood and alleviate shortness of breath.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A structured program that includes exercise training, education, and counseling to improve breathing techniques and overall physical conditioning.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered for patients with advanced COPD.
Living with COPD
Living with COPD can be challenging, but there are many strategies that individuals can adopt to improve their quality of life. This includes:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles used for breathing and improve overall lung function.
- Follow Treatment Plan: Adhering to prescribed medications and treatment regimens as directed by healthcare professionals is crucial for managing COPD effectively.
- Avoid Triggers: Minimize exposure to lung irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and chemical fumes.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to support overall health and well-being.
- Seek Support: Joining support groups or seeking counseling can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies for individuals living with COPD.
Conclusion
COPD is a chronic lung condition that requires ongoing management and support. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals with COPD can take proactive steps to improve their quality of life and maintain their independence for as long as possible. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of COPD, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With the right approach and support, living well with COPD is achievable.
<a href=”http://www.freepik.com”>Designed by Freepik</a>